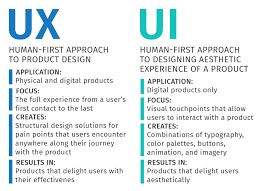
The Role of a User Interface Designer
A user interface designer plays a crucial role in the development of digital products and services. They are responsible for creating interfaces that are visually appealing, intuitive to use, and effectively communicate the purpose of the product to the end user.
One of the key tasks of a user interface designer is to ensure that the layout, color scheme, typography, and overall design elements create a seamless and enjoyable user experience. By understanding user behavior and preferences, they can design interfaces that are easy to navigate and interact with.
Collaboration with other team members, such as UX designers, developers, and product managers, is essential for a user interface designer to create cohesive designs that align with the overall goals of the project. They must also stay updated on design trends and best practices to deliver innovative solutions.
Testing and iterating on designs based on user feedback is another important aspect of a user interface designer’s role. By conducting usability tests and gathering insights from real users, they can refine their designs to enhance usability and meet the needs of the target audience.
In conclusion, a user interface designer plays a critical role in shaping the visual identity and usability of digital products. Their attention to detail, creativity, and understanding of user needs make them valuable contributors to the success of any digital project.
Top 5 Benefits of Being a User Interface Designer
- Enhances user experience through intuitive and visually appealing designs.
- Collaborates with cross-functional teams to create cohesive digital products.
- Stays updated on design trends and best practices to deliver innovative solutions.
- Conducts usability tests to gather feedback and improve interface usability.
- Plays a key role in shaping the visual identity and brand perception of products.
Challenges Faced by User Interface Designers: Navigating a Competitive and Demanding Field
- Highly competitive field with a saturated job market
- Pressure to constantly stay updated on design trends and technologies
- Balancing user preferences with client requirements can be challenging
- Subjective nature of design can lead to conflicting feedback from stakeholders
- Tight deadlines and demanding clients may result in work stress
- Limited opportunities for career advancement without expanding skill set
Enhances user experience through intuitive and visually appealing designs.
User interface designers excel in enhancing user experience through their expertise in creating intuitive and visually appealing designs. By carefully crafting interfaces that are easy to navigate and aesthetically pleasing, they ensure that users have a seamless and enjoyable interaction with digital products and services. Their focus on user-centric design principles not only improves usability but also elevates the overall satisfaction of users, making the experience more engaging and memorable. With their keen eye for detail and dedication to creating meaningful interactions, user interface designers play a vital role in shaping positive user experiences across various platforms.
Collaborates with cross-functional teams to create cohesive digital products.
A significant advantage of a user interface designer is their ability to collaborate effectively with cross-functional teams to develop cohesive digital products. By working closely with UX designers, developers, and product managers, the user interface designer ensures that the design elements align with the project’s overall goals and objectives. This collaborative approach helps in creating interfaces that not only look visually appealing but also function seamlessly to provide a positive user experience. The diverse perspectives and expertise brought together by cross-functional teams result in well-rounded and innovative digital products that meet the needs of users effectively.
Stays updated on design trends and best practices to deliver innovative solutions.
A key advantage of a user interface designer is their commitment to staying updated on design trends and best practices in order to deliver innovative solutions. By continuously learning about the latest developments in the field, they are able to incorporate cutting-edge design elements and techniques into their work. This proactive approach not only ensures that their designs remain fresh and relevant but also allows them to push the boundaries of creativity and provide clients with forward-thinking solutions that meet the evolving needs of users.
Conducts usability tests to gather feedback and improve interface usability.
One significant advantage of a user interface designer is their ability to conduct usability tests to gather valuable feedback and enhance the usability of interfaces. By engaging real users in testing scenarios, designers can identify pain points, understand user behavior, and pinpoint areas for improvement. This iterative process not only helps refine the interface design but also ensures that the final product meets the needs and expectations of the target audience. The insights gained from usability tests empower designers to make informed decisions that result in a more intuitive and user-friendly interface, ultimately enhancing the overall user experience.
Plays a key role in shaping the visual identity and brand perception of products.
A user interface designer plays a key role in shaping the visual identity and brand perception of products. By carefully crafting the visual elements of interfaces, such as color schemes, typography, and layout, they can create a cohesive and memorable brand experience for users. Through their design choices, user interface designers can evoke specific emotions, convey brand values, and establish a consistent visual language that reinforces brand recognition. This attention to detail not only enhances the overall user experience but also contributes to building a strong and recognizable brand image in the minds of consumers.
Highly competitive field with a saturated job market
In the realm of user interface design, one significant challenge lies in the highly competitive nature of the field and the saturation of the job market. With an increasing number of aspiring designers entering the industry and technological advancements driving demand for skilled professionals, standing out among the competition can be a daunting task. Job seekers may find themselves facing fierce competition for limited opportunities, requiring them to continuously hone their skills, stay updated on industry trends, and showcase their unique abilities to secure positions in this competitive landscape.
Pressure to constantly stay updated on design trends and technologies
One challenge faced by user interface designers is the pressure to continually stay abreast of evolving design trends and emerging technologies. With the digital landscape constantly evolving, designers must invest time and effort to keep their skills and knowledge up-to-date. This demand for staying current can be daunting, requiring designers to dedicate significant time to research, training, and experimentation to ensure they remain competitive in the field. Failure to stay updated may result in falling behind industry standards and losing relevance in a fast-paced and dynamic design environment.
Balancing user preferences with client requirements can be challenging
Balancing user preferences with client requirements can be a challenging aspect for user interface designers. While designers aim to create interfaces that are user-friendly and visually appealing based on user needs and behaviors, they must also consider the business goals and branding guidelines provided by the client. Striking the right balance between what users want and what clients expect can sometimes lead to compromises that may not satisfy either party completely. This delicate balancing act requires effective communication, negotiation skills, and a deep understanding of both user experience principles and client objectives to ensure that the final design meets the needs of all stakeholders involved.
Subjective nature of design can lead to conflicting feedback from stakeholders
The subjective nature of design within the realm of user interface design can often result in conflicting feedback from stakeholders. Different individuals may have varying preferences, tastes, and interpretations of what constitutes an effective design. This diversity in perspectives can lead to challenges in reaching a consensus on the best approach for a project. Balancing these conflicting viewpoints while maintaining the integrity of the design vision requires diplomacy, communication skills, and a deep understanding of how to align stakeholder feedback with the overall objectives of the project.
Tight deadlines and demanding clients may result in work stress
Tight deadlines and demanding clients can significantly contribute to work stress for user interface designers. The pressure to deliver high-quality designs within limited time frames while meeting client expectations can be challenging. Balancing creativity with efficiency under such circumstances can lead to increased stress levels and potential burnout. Managing client demands, revisions, and last-minute changes while adhering to project timelines requires strong organizational skills and the ability to work effectively under pressure. Finding ways to prioritize tasks, communicate effectively with clients, and maintain a healthy work-life balance are essential strategies for user interface designers to navigate through stressful situations in a demanding industry.
Limited opportunities for career advancement without expanding skill set
One significant challenge faced by user interface designers is the limited opportunities for career advancement without expanding their skill set. In a rapidly evolving field where new technologies and design trends emerge constantly, staying relevant and competitive requires continuous learning and upskilling. Without expanding their skill set to include emerging tools, techniques, or specialized areas of design, UI designers may find it difficult to progress to higher positions or take on more challenging projects. To overcome this con, UI designers must proactively seek out opportunities for professional development, attend workshops or courses, and stay abreast of industry trends to enhance their skills and broaden their career prospects.